Understanding Septic Systems: An Overview
What Is a Septic System? – Definition and components of a septic system
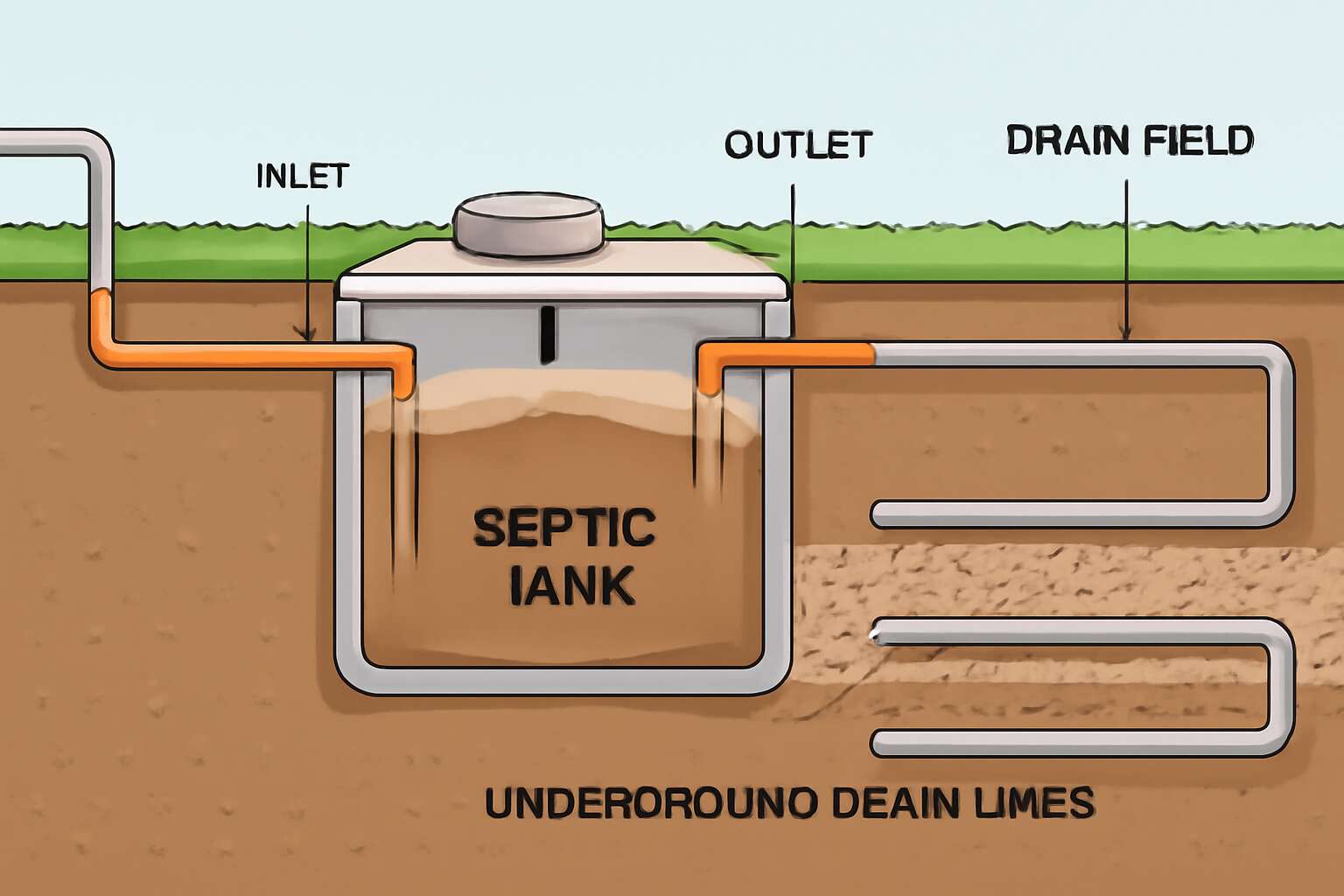
Imagine a tiny, underground city working tirelessly beneath your feet—except instead of bustling streets, you have a septic tank and drain field diagram guiding the flow of waste. This unassuming marvel of sanitation is the backbone of many South African homes that aren’t hooked up to municipal sewage systems. A septic system is essentially a self-contained waste management unit, comprising a septic tank and a drain field, designed to treat and dispose of household effluent with minimal fuss. Think of it as your home’s very own waste processing plant, complete with its own set of specialized components.
At its core, a septic system features a septic tank where solids settle and organic matter begins to decompose. The effluent then travels to the drain field—a network of perforated pipes laid in gravel trenches—where natural soil acts as the ultimate filter. To visualize this, a septic tank and drain field diagram offers a clear blueprint of how these components work harmoniously. It’s a bit like a map for your waste’s journey — from your toilet to the earth’s loving embrace.
- Septic tank: The initial waste collection chamber
- Drain field: The natural filtration zone with perforated pipes
- Soil absorption: The final step in cleaning and dispersing the water
Understanding these fundamental components is vital, especially when considering proper maintenance or troubleshooting. Whether you’re a homeowner in South Africa or just someone curious about the underground marvels, a detailed septic tank and drain field diagram is your best friend in demystifying this essential yet often overlooked infrastructure.
Why Proper Drain Field Placement Matters – Importance for system efficiency and environmental safety
Imagine your home’s waste management system as the unsung hero of sanitation—quiet, efficient, and often overlooked. A well-placed septic tank and drain field diagram isn’t just a pretty picture; it’s the blueprint that ensures everything flows smoothly beneath your feet. Proper drain field placement is critical because it directly impacts system efficiency and environmental safety. When the drain field is in the wrong spot, you risk sewage backups, groundwater contamination, and costly repairs—hardly the kind of drama anyone wants.
In South Africa, where many homes rely on septic systems, understanding the nuances of drain field placement can make or break your waste disposal. An optimized layout guarantees the natural soil acts as a filter, dispersing effluent safely into the earth. It’s not just about avoiding unpleasant surprises but about protecting your property and the environment. A detailed septic tank and drain field diagram becomes your trusty map, guiding you through the underground labyrinth with clarity and confidence.
Ultimately, thoughtful placement isn’t just good sense; it’s an investment in the longevity and safety of your septic system. Remember, the secret to a happy, healthy septic system lies beneath the surface—where a well-designed drain field does the heavy lifting, keeping everything flowing in harmony.
Common Types of Septic Systems – Different system configurations and their applications
Septic systems are often the silent guardians of sanitation in many South African homes, quietly working beneath the surface. But did you know that understanding the different types of septic systems can significantly influence their longevity and environmental safety? Each configuration is designed with specific land conditions and household needs in mind, making the right choice crucial. The septic tank and drain field diagram serve as essential tools, revealing the intricate underground network where waste transforms from raw sewage into harmless effluent.
Among the common types of septic systems are:
- Conventional systems with gravel-filled drain fields
- Chamber systems that allow for easier installation and maintenance
- Aerobic treatment units that incorporate oxygen to accelerate waste breakdown
Applying the correct configuration depends on factors like soil type, space availability, and local regulations. This is where a detailed septic tank and drain field diagram becomes invaluable—guiding homeowners and professionals alike through the complex process of site planning and system installation. Ultimately, choosing the right system and understanding its layout can make all the difference in preventing costly failures and safeguarding the environment.
Components of a Septic Tank and Drain Field
Septic Tank Components – Inlet and outlet pipes, baffles, filters, and tank material
When it comes to understanding your septic system, knowing the components of a septic tank and drain field diagram can feel like deciphering ancient hieroglyphs—except it’s actually straightforward once you get the hang of it! The septic tank itself is a marvel of engineering, designed to hold and treat wastewater from your home. It features crucial parts like inlet and outlet pipes that guide effluent smoothly in and out, preventing any messy mishaps. Baffles are installed to stop solids from rushing straight into the drain field, protecting the entire system from clogging. Filters, often overlooked, act as the system’s gatekeepers, catching debris before it can cause trouble downstream. The tank material, whether concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene, plays a role in durability and longevity—think of it as the septic system’s armor against the South African elements.
Understanding these components is key to visualizing a septic tank and drain field diagram, especially when considering maintenance or troubleshooting. It’s a delicate dance of water and waste, all housed within a structure that’s surprisingly resilient. As vital as the plumbing in your home, these parts work tirelessly to keep your waste management efficient and environmentally safe. A clear diagram isn’t just a pretty picture—it’s a vital blueprint for keeping your septic system functioning flawlessly for years to come!
Drain Field Components – Distribution pipes, gravel/stone bed, and soil absorption system
The septic tank and drain field diagram reveal a hidden symphony of engineering mastery beneath the surface—a delicate choreography of water, waste, and nature working in harmony. At the heart of this system, the distribution pipes serve as arteries, channeling effluent with precision into the gravel and stone bed, a crucial component of the drain field. This layer acts as a natural filter, where the liquid begins its slow, deliberate journey into the soil. The soil absorption system then takes center stage, employing the earth’s innate ability to purify wastewater, transforming it into safe, clean groundwater.
- Distribution pipes
- Gravel and stone bed
- Soil absorption system
Each element relies on the next, creating a resilient network that maintains environmental integrity and system longevity. Understanding these drain field components illuminates the intricate dance that keeps South African homes functioning seamlessly, all depicted vividly in a well-crafted septic tank and drain field diagram. It’s more than plumbing—it’s a testament to nature’s quiet, relentless power working tirelessly beneath our feet.
Additional System Elements – Vent pipes, inspection ports, and pumps (if applicable)
Beyond the core components of a septic tank and drain field diagram, several additional system elements are vital for ensuring seamless operation and longevity. Vent pipes, for instance, act as the system’s respiratory system—allowing gases to escape safely while preventing unpleasant odors from seeping into living spaces. These pipes are often discreetly positioned but are crucial for maintaining proper airflow, which in turn prevents pressure buildup that can compromise the entire system.
Inspection ports are another unsung hero in septic system maintenance. Strategically placed access points enable professionals to monitor, inspect, and clean the tank and associated components without invasive excavation. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues early, saving homeowners from costly repairs down the line. Pumps, although not always necessary, can be a game-changer in systems where gravity flow isn’t sufficient. Especially in hilly terrains or areas with high water tables, pumps ensure the effluent moves smoothly from the septic tank into the drain field.
- Vent pipes
- Inspection ports
- Pumps (if applicable)
Understanding these additional elements within a septic tank and drain field diagram highlights the complexity and precision behind what many consider a simple waste management system. Each piece plays a pivotal role in safeguarding environmental health and ensuring a home’s plumbing remains resilient over decades. When viewed collectively, these components form a resilient network—one that cleverly balances engineering ingenuity with the earth’s natural filtration processes.
Visualizing the Septic Tank and Drain Field Diagram
Basic Septic System Layout – Typical diagram with key components labeled
In the quiet tapestry of rural South Africa, where every drop of water whispers life back into the earth, visualizing the septic tank and drain field diagram transforms from mere schematic to a poetic dance of function and form. Imagine a blueprint where each component plays its part—like the heart’s chambers—pumping, filtering, and releasing life’s essential waste with meticulous grace. The typical diagram reveals the septic system’s soul: the tank, with its inlet and outlet pipes, stands as a guardian of waste, while the drain field unfolds like roots reaching deep into the soil, distributing and absorbing with natural precision.
Understanding this schematic is akin to reading a map of underground currents—an intricate web where the septic tank’s baffles and filters guide waste into a network of distribution pipes, nestled within gravel or stone beds. This orchestrated layout ensures that the soil’s absorption system does its silent work, safeguarding both environment and health. When you visualize the septic tank and drain field diagram, you see not just components, but a symphony of ecological balance, crafted to serve communities with silent efficiency and enduring resilience.
Design Considerations – Spacing, depth, and size based on household needs
Visualizing the septic tank and drain field diagram involves more than just understanding a simple schematic; it’s about perceiving a carefully orchestrated ecosystem beneath the earth’s surface. When designing this system, considerations of spacing, depth, and size become vital—each tailored to the household’s unique needs. In the heart of rural South Africa, these parameters transform into a symphony of ecological harmony, ensuring waste is managed efficiently and safely.
The size of the septic tank, for instance, depends on the household size and water usage patterns—larger families demand larger tanks to prevent overflow and ensure proper treatment. Depth placement also influences system longevity, with typical installations ranging from 1 to 3 meters below ground, safeguarding against surface disturbances and seasonal variations. Proper spacing between the septic tank and the drain field ensures optimal absorption and reduces the risk of contamination. When these elements are thoughtfully calibrated, the septic system functions as a resilient, silent guardian of community health.
For those envisioning their septic tank and drain field diagram, it’s helpful to remember that these components are interconnected—like the veins of a living organism. An understanding of the nuanced relationship between size, spacing, and depth will illuminate the path toward a sustainable and efficient design, crafted to serve both the environment and the people who depend on it. In this delicate underground dance, every measurement influences the system’s ability to perform its vital role—keeping soil and water safe for generations to come.
Flow of Wastewater – Diagram of how wastewater moves through the system
Visualizing the flow of wastewater through a septic tank and drain field diagram reveals a complex yet elegant journey—an underground ballet of clean, controlled movement. As wastewater exits the household, it first enters the septic tank, where solids settle, allowing the liquid to flow seamlessly toward the drain field. This transition is crucial, as it ensures that only treated effluent reaches the soil, safeguarding both health and the environment.
Within the septic tank, inlet and outlet pipes guide this flow, while baffles prevent solids from escaping. The liquid then travels through distribution pipes laid out in the drain field—a carefully engineered network of gravel and soil absorption beds designed for optimal filtration. This interconnected system relies on precise spacing and depth, which are visually represented in a septic tank and drain field diagram, capturing the harmony between engineering and ecology.
Understanding this flow underscores the importance of each component working in concert. When properly visualized, the septic system becomes less a mysterious underground entity and more a vital part of sustainable living—an intricate dance of waste management that quietly preserves the health of communities and the land they cherish.
Interpreting the Drain Field Diagram
Drain Field Layout – Typical arrangement of drain pipes and absorption beds
In the shadowed realm of subterranean architecture, the septic tank and drain field diagram reveals a mysterious ballet of waste and absorption, orchestrated beneath the earth’s surface. This blueprint, often overlooked, encodes the silent story of how effluent disperses into nature’s hidden corridors. Understanding the layout of a drain field is akin to deciphering an ancient map—each pipe, gravel bed, and absorption zone playing a vital role in the symphony of waste management.
The typical arrangement of drain pipes and absorption beds can be visualized as a labyrinthine network, carefully designed to maximize efficiency while blending seamlessly into the landscape. The drain field layout often features a series of perforated pipes laid within gravel or stone beds, which facilitate the gradual seepage of effluent into the soil. These components are arranged to ensure that waste is evenly distributed, preventing saturation and environmental contamination.
By interpreting the septic tank and drain field diagram, one can discern the flow of wastewater—how it exits the tank, travels through the network of pipes, and finally dissolves into the earth’s embrace. This understanding is crucial for ensuring the longevity and safety of the system, especially in regions like South Africa, where the land’s resilience is tested against modern demands. The layout’s precision, from spacing to depth, echoes the delicate balance required to keep this underground ecosystem functioning optimally.
Soil and Landscape Factors – How soil type and terrain influence design
Within the intricate tapestry of subterranean engineering, the septic tank and drain field diagram is a poetic map of unseen harmony. It reveals how the soil’s silent language influences the very essence of wastewater dispersal. Soil type and terrain are not mere backdrops but active players—dictating the dance of effluent as it journeys toward absorption. In South Africa’s diverse landscape, understanding these factors becomes vital to designing a resilient septic system that endures the land’s temperament.
Clay soils, with their dense embrace, act as a slow but steadfast gatekeeper—requiring wider absorption beds to prevent saturation. Conversely, sandy soils, with their eager permeability, demand meticulous control of flow rates to avoid rapid seepage and potential contamination. The terrain’s slope also guides the layout; gentle inclines favor even distribution, while steep slopes challenge the placement of the septic tank and drain field components. Recognizing these nuances ensures the septic tank and drain field diagram aligns perfectly with nature’s unique contours, fostering an underground ecosystem that functions harmoniously with South Africa’s varied landscapes.
By considering soil and landscape factors, engineers craft designs that optimize the septic system’s longevity and environmental safety. The delicate balance of spacing, depth, and material selection hinges on these natural characteristics, transforming a simple diagram into a living blueprint—an ode to the land’s resilience and the ingenuity of human adaptation. Every perforated pipe and gravel bed becomes a testament to the symbiotic relationship between technology and earth, vital for sustainable waste management in this vibrant region.
Common Signs of System Issues – Visual cues and diagram warnings
Sometimes, your septic system throws a tantrum—without warning, of course. Recognizing the early signs of system issues can save you from a messy, costly disaster. Visual cues are your best allies here, acting like the system’s own Morse code. Cracks in the yard, foul odors wafting unexpectedly, or lush, green patches in the midst of a brown landscape are telltale signs that something’s amiss with your septic tank and drain field diagram.
Careful inspection of the diagram can reveal warning flags—such as inconsistent flow patterns or blocked pipes—that hint at underlying problems. Pay close attention to any standing water or soggy areas, which often indicate that the effluent isn’t dispersing as it should. It’s not just about aesthetics; these symptoms threaten environmental safety and the longevity of the system. Remember, the diagram isn’t just a pretty picture—it’s a roadmap to understanding what’s happening beneath the surface.
In the realm of septic systems, being vigilant can be the difference between smooth operation and a septic emergency. Look for:
- Unusual odors near the septic tank or drain field
- Slow-draining sinks and toilets
- Persistent wet patches that refuse to dry out
- Sudden lush patches of grass or vegetation that outshine the rest of the yard
Understanding these signs in conjunction with your septic tank and drain field diagram ensures you catch issues early—saving time, money, and the environment from unnecessary strain. After all, the health of your septic system is directly linked to how well you interpret its silent signals!
Creating an Effective Septic System Diagram
Elements to Include – Accurate placement of tank, pipes, and drain field
Creating an accurate septic tank and drain field diagram is essential to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your septic system. When designing this diagram, every element must be precisely placed—misalignment can lead to costly repairs and environmental hazards. To achieve this, consider the natural landscape and soil conditions, which heavily influence the placement of the tank and drain field.
Key elements to include in your septic tank and drain field diagram are the exact location of the septic tank, the flow of wastewater from the household, and the layout of distribution pipes in the drain field. Proper depiction of these components helps visualize how waste moves through the system, preventing potential blockages or failures.
Incorporate details such as:
- The position of inlet and outlet pipes
- Placement of distribution trenches
- Soil absorption areas and gravel beds
By ensuring these elements are accurately represented and thoughtfully arranged, you create a blueprint that not only guides installation but also safeguards your property’s health and the environment. The septic tank and drain field diagram becomes more than just a schematic—it becomes a vital tool for maintaining system integrity and avoiding future problems.
Scale and Measurements – Ensuring the diagram is proportional and detailed
In the shadowed realm of waste management, a meticulously scaled septic tank and drain field diagram is the silent guardian of longevity and harmony within your property’s underground labyrinth. When crafting this blueprint, every measurement must echo with precision—an imbalance can trigger catastrophic failures or environmental ruin. The secret lies in translating the natural landscape’s subtle whispers—soil absorption rates, terrain contours—into a detailed, proportional sketch that guides installation with unwavering accuracy.
Imagine the flow of waste as a dark, winding river—its course charted through inlet and outlet pipes, traversing distribution trenches, and nestled within gravel beds designed for optimal absorption. To attain this level of detail, consider incorporating numbered measurements and scaled representations of key components, such as:
- The exact position of the septic tank
- The pathways of wastewater flow
- The layout of distribution pipes and absorption areas
Such an approach ensures your septic tank and drain field diagram isn’t merely a schematic but a vital map—one that preserves the integrity of the system and guards against unseen, creeping failures beneath the earth’s surface.
Precision in scale and measurement transforms a simple diagram into a living, breathing blueprint—a blueprint that reveals the subtle interplay between soil, landscape, and the subterranean flow of waste, ensuring your septic system’s silent vigil remains unbroken for years to come.
Tools and Software – Digital options for designing septic system diagrams
Creating an effective septic tank and drain field diagram requires more than just sketching outlines; it demands a symphony of precision and digital finesse. In the digital age, harnessing specialized tools and software transforms what could be a rudimentary schematic into an intricate, exact blueprint that captures every nuance of underground infrastructure. This process is crucial in South Africa, where diverse soil types and terrain can dramatically influence system performance.
Modern design software like AutoCAD Civil 3D, SketchUp, or specialized septic design programs offer robust features tailored to this task. These tools enable the integration of real-world measurements with layered components—capturing the precise position of the septic tank, wastewater pathways, and drainage trenches. Such detailed digital models serve as vital guides, ensuring each element aligns seamlessly with landscape and soil absorption rates.
Incorporating digital options for designing septic system diagrams not only enhances accuracy but also simplifies updates—an essential attribute when adapting to site-specific variables. The ability to visualize the entire system in a three-dimensional space fosters a deeper understanding of how waste flows through the underground labyrinth, making the difference between a fragile setup and one built for enduring reliability.
Whether opting for CAD-based platforms or user-friendly septic system design software, the goal remains the same: to craft a detailed, proportionally scaled septic tank and drain field diagram that becomes an indelible blueprint, safeguarding the system’s longevity and environmental harmony. In this meticulous digital realm, every line and measurement echoes with purpose, transforming complex underground interactions into a clear, navigable map—one that whispers secrets of resilience and harmony beneath the surface.
Benefits of a Detailed Septic Tank and Drain Field Diagram
Maintenance and Troubleshooting – Using diagrams for system inspection and repairs
In the silent depths of a septic system, where unseen forces work tirelessly, a detailed septic tank and drain field diagram becomes an invaluable map. It offers a window into the system’s intricate architecture, revealing how each component interacts in harmony—or discord. When maintenance or troubleshooting beckons, this visual guide transforms into a powerful tool, allowing professionals and homeowners to pinpoint issues with precision.
Using diagrams for system inspection and repairs not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes the risk of unforeseen failures. For example, understanding the exact placement of the inlet and outlet pipes within the septic tank can prevent costly damage. Moreover, a well-crafted septic tank and drain field diagram provides clarity in complex scenarios, guiding repairs and ensuring the longevity of the entire system. It’s a silent guardian—an essential blueprint that safeguards the health of both the environment and those who rely on it.
In essence, a comprehensive diagram isn’t just technical documentation; it’s a narrative of trust and foresight. It empowers us to see beyond the surface, embracing the subtle artistry behind wastewater management. With this knowledge, we can anticipate issues before they manifest, ensuring the septic system remains a silent, yet vital, part of our lives.
Permit and Inspection Processes – Supporting documentation for regulatory compliance
A detailed septic tank and drain field diagram is more than just a technical sketch; it’s a vital document for permit and inspection processes. Regulatory agencies often require comprehensive diagrams to verify system compliance with local standards. These diagrams provide clear evidence that the installation adheres to environmental safety regulations and health codes, streamlining approval procedures.
Supporting documentation with precise placement of components—such as inlet and outlet pipes, distribution chambers, and soil absorption beds—can significantly reduce delays. When authorities review a well-crafted septic tank and drain field diagram, they gain confidence in the system’s design and safety. This ensures that your property meets all legal requirements and minimizes the risk of costly rework.
Plus, an accurate diagram can serve as a safeguard during inspections, helping to quickly identify potential issues. In South Africa, where environmental protection is paramount, having thorough documentation like a septic tank and drain field diagram is essential for a smooth permit and inspection process. It’s a cornerstone of responsible wastewater management, protecting both the environment and property owners.
Design Optimization – Improving system lifespan and efficiency through accurate diagrams
Within the shadowed corridors of wastewater management lies a secret weapon: the detailed septic tank and drain field diagram. This blueprint, carved with precision, transforms chaos into order, ensuring every component is placed with unwavering accuracy. Such meticulous design not only safeguards the environment but also extends the lifespan of the entire system, weaving longevity into its very fabric.
A well-crafted diagram reveals the intricate dance of inlet and outlet pipes, distribution chambers, and soil absorption beds—each element aligned to optimize flow and efficiency. When these elements harmonize, the septic system breathes easier, functioning seamlessly for years to come. The power of precise placement and scale ensures that the system’s performance is maximized, reducing the need for costly repairs and invasive interventions.
In the silent depths of the earth, where unseen forces govern, a detailed septic tank and drain field diagram becomes an unerring compass—guiding installations, maintenance, and troubleshooting with unwavering clarity. It’s a vital relic of responsible wastewater management, safeguarding South Africa’s precious environment and the sanctity of property alike.

0 Comments